نمایش نتیجه 2121 تا 2130 از 2718 نتیجه یافت شده برای v:
n: any of various materials, such as mica flakes or walnut hulls, that cure lost circulation. See lost circulation. lost circulation materials.
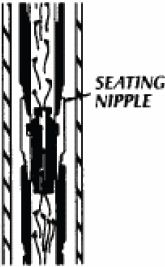
n: a special tube installed in a string of tubing, having matching wireline tool with locking pawls. It is used to hold a regulator, choke, or safety valve;to anchor a pump;or to permit installation of gas lift valves. Also called a landing nipple.
a machined profile in a heavy wall short tubing section that allows a plug to be set and the seal on the plug to effectively isolate the well.
n: porosity created in a formation after it has formed, because of dissolution or stress distortion taking place naturally, or because of treatment by acid or injection of coarse sand.
non intergranular porosity such as fractures, vugs, etc. that may contribute sharply to permeability but may not significantly raise the porosity level.
n: a standard die value of which is fixed by direct or indirect comparison with a primary standard or by means of a reference-value standard. Compare primary standard. working standard
n: the time in seconds that it takes 1 quart of drilling mud to flow out of a Marsh funnel. It is a measure of the muds viscosity. See also Marshfunnel.
n: 1. a unit of land measurement in the rectangular survey system. Each 6-mile (9.7-kilometre) square, or township, is divided into 36 sections. A section usually is 1 square mile (2,590 square kilometres),or 640 acres (256 hectares). It may be larger or smaller, depending on its position in the township. 2. vertically arrayed data.
n: the sediment in oil or other liquid that tends to adhere, or cling, to the side of a tank or vessel.
introducing very small particles in the liquid that accelerate the development of scale or other precipitates.
adj: of or relating to an earthquake seismograph indicate the general characteror earth vibration, including those artificially induced.
an exploration technique that can find structures and potential reservoir traps by reflecting sound waves from the rock strata. [Seismic acquisition (2-D, 3-D, 4-D) – seismic data are used to map subsurface formations. A 2-D survey reveals a cross section
n: see well velocity survey.